Sound Therapy for Tinnitus: A Comprehensive Guide
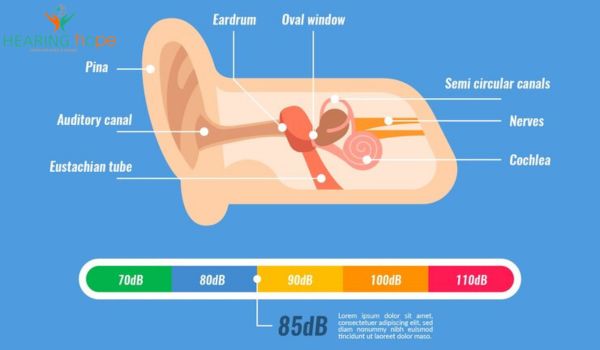
Sound Therapy for Tinnitus: A Comprehensive Guide Tinnitus, commonly described as persistent ringing, buzzing, or humming in the ears, impacts millions worldwide, often disrupting daily life. This auditory condition can lead to challenges such as stress, difficulty concentrating, and sleep disturbances. While it may not have a definitive cure, tinnitus sound therapy has emerged as a highly effective solution for managing symptoms and improving overall well-being. By utilizing external sounds, sound therapy helps mask or retrain the brain’s response to tinnitus, offering relief and fostering a better quality of life. In this detailed guide, we will delve into the science behind sound therapy for tinnitus, explore its various types, and highlight the benefits it provides for tinnitus sufferers. Additionally, we will share actionable tips to seamlessly integrate sound therapy into your routine, helping you take control of tinnitus and enjoy a more peaceful auditory experience. What is Tinnitus? Tinnitus refers to hearing sounds, such as ringing or buzzing, without any external source. The sounds may vary in tone, frequency, and intensity, often described as ringing, humming, or buzzing. It can affect one or both ears and ranges from temporary to chronic conditions. Common Causes of Tinnitus Hearing Loss: Age-related or noise-induced hearing loss is a major cause. Ear Infections or Blockages: Wax buildup, infections, or fluid in the ear can trigger tinnitus. Stress and Anxiety: These amplify the perception of tinnitus symptoms. Medications: Certain drugs, such as aspirin or antibiotics, may worsen tinnitus. What is Sound Therapy for Tinnitus? Sound therapy involves the use of external sounds to manage tinnitus symptoms. Introducing controlled auditory stimuli helps mask or retrain the brain’s response to internal ringing or buzzing. How Sound Therapy Works Masking: External sounds reduce the prominence of tinnitus, providing immediate relief. Habituation: Over time, the brain learns to ignore tinnitus, minimizing its impact. Relaxation: Calming sounds alleviate stress, which often worsens tinnitus symptoms. Types of Sound Therapy Understanding the various types of sound therapy can help you choose the best approach for your tinnitus management. Masking Therapy Uses devices like white noise machines or mobile apps to mask tinnitus sounds. Best suited for mild to moderate tinnitus cases. Tinnitus Retraining Therapy (TRT) Combines sound therapy with counseling to retrain the brain’s perception of tinnitus. Ideal for long-term management and reducing emotional distress. Neuromodulation Targets specific auditory nerve signals with customized sound frequencies. Effective for persistent tinnitus conditions. Natural Sound Therapy Utilizes nature-inspired sounds like rain, waves, or birdsong to promote relaxation. Particularly beneficial for stress-induced tinnitus. Hearing Aids with Sound Therapy Features Amplify external sounds while masking tinnitus. Useful for individuals with both hearing loss and tinnitus. Therapy Type Key Features Best For Masking Therapy Uses white noise or pink noise Mild to moderate tinnitus Tinnitus Retraining Therapy Combines sound with counselling Chronic tinnitus Neuromodulation Customized auditory nerve stimulation Persistent tinnitus Natural Sound Therapy Uses nature-inspired sounds Stress-induced tinnitus Hearing Aids with Therapy Amplifies sound, masks tinnitus Hearing loss with tinnitus Benefits of Sound Therapy for Tinnitus Immediate Tinnitus Relief: Sound therapy provides instant relief by masking the intrusive sounds of tinnitus with calming or white noise. This immediate effect helps reduce frustration and anxiety caused by persistent ringing or buzzing. Improved Sleep Quality: Soothing sounds, such as ocean waves or gentle rain, create a tranquil atmosphere that promotes deep, uninterrupted sleep. This is particularly beneficial for tinnitus sufferers who struggle with sleep disturbances. Enhanced Focus and Productivity: By minimizing the constant distraction of tinnitus, sound therapy allows individuals to focus better on work or daily activities. This improvement in concentration significantly enhances productivity and efficiency. Stress Reduction: Relaxing auditory experiences offered by sound therapy help lower stress and anxiety levels. Since stress often exacerbates tinnitus, this calming effect plays a crucial role in symptom management. Long-term Brain Habituation: Regular use of sound therapy retrains the brain to adapt to tinnitus sounds, effectively ignoring them over time. This process, known as habituation, leads to lasting relief from symptoms. Customizable Solutions: Sound therapy can be tailored to individual needs with options like white noise, nature sounds, or personalized tones. This flexibility ensures a more comfortable and effective experience for every user. Non-invasive and Safe: Unlike medications or invasive treatments, sound therapy is a completely safe and non-invasive approach to managing tinnitus. It carries no side effects, making it suitable for long-term use. Support for Emotional Well-being: The calming nature of sound therapy contributes to better emotional health by reducing irritability and enhancing relaxation. This helps individuals cope more effectively with the psychological challenges of tinnitus. Tips for Selecting the Most Effective Sound Therapy for Tinnitus Selecting the right sound therapy involves evaluating personal needs, severity, and lifestyle preferences. Identify Your Tinnitus Type: Determine whether your tinnitus is stress-induced, noise-related, or linked to hearing loss. Consult a Specialist: A professional audiologist can assess your condition and recommend the best therapy. Try Different Therapies: Experiment with various methods, from white noise machines to hearing aids, to identify what works best. Innovative Sound Therapy Tools and Devices Modern technology has revolutionized sound therapy with advanced tools and applications. Mobile Apps: Apps like Resound Relief offer customizable masking sounds and relaxation exercises. White Noise Machines: Portable devices generate calming sounds like rain, ocean waves, or fan noises. Hearing Aids: Hearing aids with built-in sound therapy provide dual benefits of amplification and tinnitus management. Wearable Sound Generators: Discreet devices that deliver continuous sound therapy throughout the day. Tips for Effective Sound Therapy Maximize the benefits of sound therapy with these tips: Consistency: Use sound therapy daily to reinforce habituation. Pair with Relaxation Techniques: Combine with meditation or breathing exercises for enhanced results. Monitor Progress: Keep track of symptom changes and adjust therapy accordingly. Create a Comfortable Environment: Ensure minimal background noise during sessions. When to Seek Medical Attention? While sound therapy can alleviate tinnitus symptoms, certain situations warrant professional care. Seek medical help if: Symptoms persist for more than a week. You experience pain, fluid discharge, or hearing loss. There are signs of underlying conditions