Exploring the Human Hearing Range: Frequencies, Limits, and Care
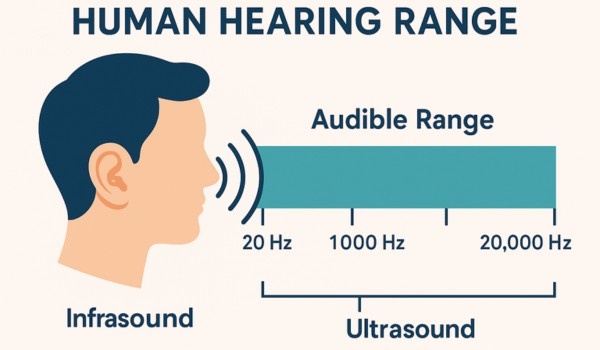
Our ears can hear a wide variety of sounds—from the low rumble of thunder to the soft chirping of birds. This ability is called the range of human hearing, which goes from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. It helps us enjoy music, understand speech, and stay aware of our surroundings.
Knowing how this range works is important for keeping our hearing healthy. Things like growing older, being around loud noises, and having certain health conditions can change how well we hear different sounds.
In this blog, we’ll explain the three parts of the hearing range: low, mid, and high frequencies. You’ll also learn what affects your hearing and how to take care of it. We’ll share simple tips and the importance of regular hearing checkups.
Whether you’re just curious or want to protect your hearing as you age, this guide will help you understand your ears better and keep them working well for years to come.
Understanding the Range of Human Hearing
The range of human hearing encompasses sounds of varying frequencies and intensities. Frequency, measured in Hertz (Hz), refers to the pitch of a sound, whether it is high or low. Loudness, measured in decibels (db), determines how soft or loud a sound is. Below is a breakdown of the human auditory range by frequency.
Low Frequencies (20 Hz–250 Hz)
Low-frequency sounds are often described as deep and rumbling. They include:
- Examples: The hum of a bass guitar, the roar of a lion, or distant thunder.
- Importance: These sounds add depth to music and help us sense our environment, even when we can’t see.
Mid Frequencies (250 Hz–4,000 Hz)
Mid-range frequencies are essential for communication and environmental awareness:
- Examples: Human speech, birdsong, and everyday sounds like ringing phones.
- Importance: This range is critical for understanding conversations and distinguishing familiar noises.
High Frequencies (4,000 Hz- 20,000 Hz)
High frequencies contribute to clarity and detail in what we hear:
- Examples: The rustling of leaves, high notes of a piano, and smoke alarm beeps.
- Importance: These frequencies enhance our ability to pick up subtle details, making sounds more realistic and defined.
Read about: What level of hearing loss requires a hearing aid to better understand when professional help is needed to improve hearing clarity and comfort.
Factors That Affect the Human Hearing Range
Your ability to hear sounds can change for different reasons. These factors can affect how loud or clear sounds are and what pitches (high or low tones) you can hear.
- Age: As we get older, we often lose the ability to hear high-pitched sounds. This often begins in your 30s or 40s and tends to become more noticeable by the time you reach 60.
- Loud Noises: Listening to loud sounds for a long time—like music through headphones or noise at work—can harm your ears. This may cause ringing in the ears or make it hard to hear clearly.
- Health Problems: Conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and some medicines can hurt the tiny parts of the ear or nerves, making hearing worse.
- Genetics: Some people are born with good or poor hearing. Family history can also affect your hearing ability.
- Environment: Living or working in noisy places like cities or factories can reduce your hearing over time.
- Habits and Lifestyle: Smoking and a poor diet can damage your ears. A healthy diet and regular exercise can help protect your hearing.
The Importance of Protecting Your Hearing
Maintaining your hearing health is vital for ensuring a rich auditory experience throughout your life. Here are some practical tips:
Daily Precautions
- Use Ear Protection: Wear earplugs or noise-cancelling headphones in loud environments.
- Limit Volume Levels: Keep headphone volumes below 60% and take breaks to give your ears a rest.
- Avoid Prolonged Exposure: Reduce time spent in noisy places or use protective measures.
Lifestyle Tips
- Healthy Diet: Nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins A, C, and E, and magnesium support ear health.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking reduces blood flow to the ear, increasing the risk of hearing damage.
How to Monitor and Maintain Your Hearing Health
Taking care of your hearing is just as important as looking after your overall health. High-frequency hearing loss can happen slowly and often goes unnoticed until it starts affecting your daily life. Here’s how you can keep your hearing in check:
Routine Testing
Schedule regular hearing tests, especially if:
- You struggle to follow conversations
- You often increase the volume on the TV or phone.
Early detection helps manage hearing loss before it worsens.
Early detection helps manage hearing loss before it worsens. If you’re unsure where to begin, consider booking a Hearing Test in Delhi to get a clear understanding of your hearing health.
Professional Care
Visit a qualified audiologist for a full hearing check-up. They can:
- Offer lifestyle tips to protect your hearing
- Measure your hearing ability with a Hearing Test for accurate results
- Suggest hearing aids if needed and guide
- you on how to put in a hearing aid correctly
Conclusion
The range of human hearing is a fascinating spectrum that allows us to experience the world through sound. However, this incredible ability is vulnerable to factors like ageing, noise exposure, and health conditions. By understanding the human auditory range and taking proactive steps to protect your hearing, you can preserve this vital sense for years to come.
Regular check-ups and consultations with audiologists are critical for identifying and managing potential hearing issues. Whether it’s safeguarding against environmental risks or addressing early signs of hearing loss, a commitment to auditory health is essential.
Frequently Asked Questions
A good hearing range for humans typically spans frequencies from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. This range allows individuals to perceive a wide array of sounds, from the lowest bass notes to the highest pitches. However, as people age, their ability to hear higher frequencies often diminishes, with many adults experiencing a reduced upper limit around 14,000 Hz or lower.
Exposure to a 10,000 Hz frequency can have varying effects depending on the context. In clinical settings, ultra-high-frequency deep brain stimulation (DBS) at 10,000 Hz has been studied for its potential to improve motor functions in individuals with movement disorders. Conversely, in therapeutic or relaxation practices, listening to 10,000 Hz tones is sometimes associated with promoting mental clarity or relaxation, though scientific evidence supporting these claims is limited.
The human ear can typically detect sounds ranging from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. Frequencies below 20 Hz are termed infrasound, and those above 20,000 Hz are called ultrasound; both are generally inaudible to humans.
The normal hearing range for humans encompasses frequencies from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. This range enables the perception of various sounds essential for communication and environmental awareness. It’s important to note that this range can vary among individuals and may decrease with age or due to prolonged exposure to loud noises.
Under ideal conditions, some individuals, particularly children and young adults, may perceive frequencies slightly above 20,000 Hz, potentially up to 22,000 Hz. However, such sensitivity is uncommon, and the standard upper limit for human hearing is generally accepted to be 20,000 Hz.
Dr. Harshi, is an accomplished Audiologist with extensive expertise in treating individuals with hearing impairments.

